HIT - Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Test (5)
Lateral Flow Assay designed for the detection of IgG antibodies against PF4/polyanion-complexes in human citrated plasma or serum.
This product is only available in Germany!
Lateral Flow Assay designed for the detection of IgG antibodies against PF4/polyanion-complexes in human citrated plasma or serum.
This product is only available in Germany!
IgG antibodies are resposible for the heparin induced thrombocytopenia.
Immobilized anti-human IgG on the membrane of the test unit binds patients IgG-antibodies which are previously captured by the PF4/polyanion-complex which is detected by intensely colored gold nanoparticles.
The presence of PF4/polyanion-complex becomes visible at a colored test line. The surplus of gold particles continues to migrate through the membrane and is captured at the control line by specific antibodies.


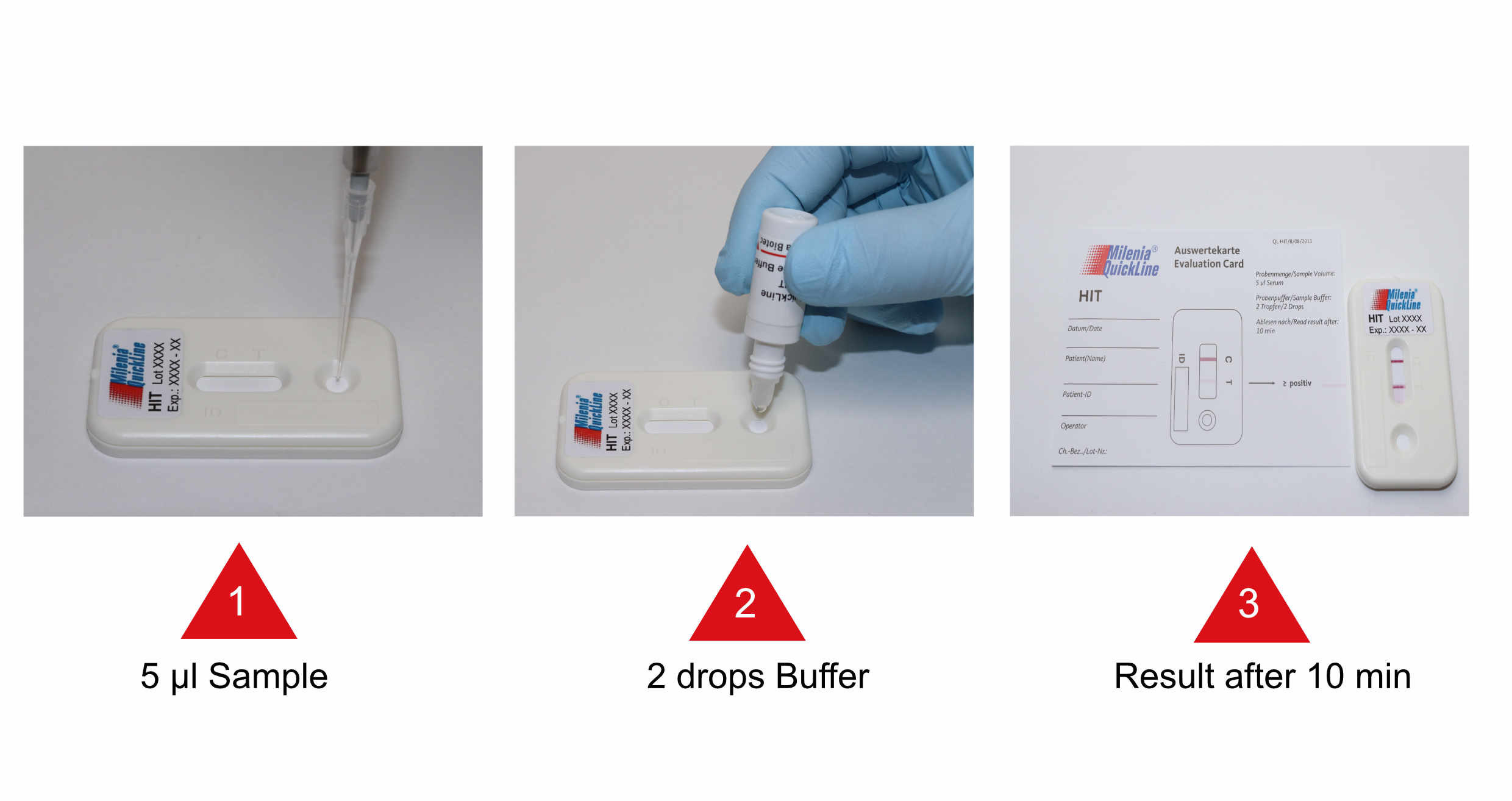
- Pipette 5 µl Serum or citrated plasma on the sample application port of the test unit
- Add 2 Drops of sample Buffer
- Let the test incubate for 10 minutes at room temperature
- Interpretation of results
2°C to 8°C
Test Unit, Sample Buffer, Evaluation cards
-
American College of Chest Physicians.Treatment and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008 Jun;133(6 Suppl):340S-380S. (2008)
Warkentin TE, Greinacher A, Koster A, Lincoff AM.
-
Evaluation of a new nanoparticle-based lateral-flow immunoassay for the exclusion of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). J Thromb Haemost. 2011; 106(6). (2011)
Sachs UJ, von Hesberg J, Santoso S, Bein G, Bakchoul T.
-
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 2009; 7 Suppl 1:9-12 (2009)
Greinacher A.
-
Prospective evaluation of PF4/heparin immunoassays for the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7 (8):1260-5. (2009)
Bakchoul T, Giptner A, Najaoui A, Bein G, Santoso S, Sachs UJ.
-
The Costs of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: a patient-based cost of illness analysis. J Throm Haemost. 2009; 7(5):766-73. (2009)
Wilke T, Tesch S., Scholz A., Kohlmann T., Greinacher A.